Brain Aneurysm: Early Signs, Symptoms, Causes & Treatment
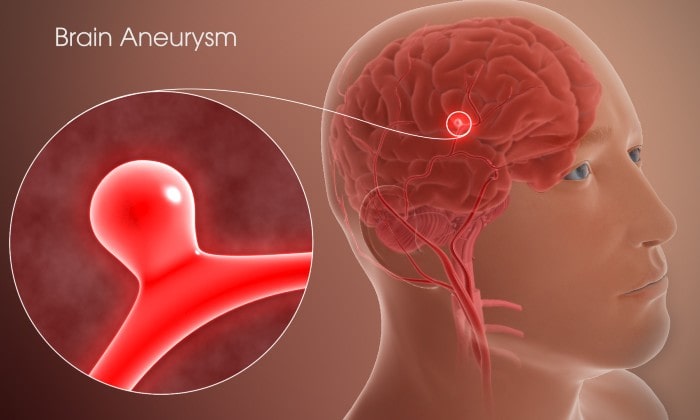
A brain aneurysm can be called ballooning or bulge in the brain's blood vessels.
An aneurysm in the brain can rupture or leak, leading to bleeding in the cerebral cortex (hemorrhagic stroke). A ruptured brain aneurysm is found within the brain's space and between tissue that surrounds the brain. This kind of hemorrhagic stroke can be known as subarachnoid hemorrhage.
Aneurysms that rupture quickly become life-threatening and require prompt medical intervention.
However, a majority of brain aneurysms aren't ruptured and don't result in health issues or symptoms. Aneurysms of this kind are usually discovered when tests are conducted for other illnesses.
Treatment for an unruptured brain aneurysm could be beneficial in certain situations and could stop a rupture shortly. Talk to your physician to make sure you know the best choices for your requirements.
Symptoms
Common symptoms and signs of ruptured aneurysms are:
- Extremely severe, the sudden headache that is highly severe and sudden
- Nausea and vomiting
- Stiff neck
- Double or blurred vision
- Sensitivity to light
- Seizure
- Drooping eyelids
- The loss of consciousness
- Confusion
- Extremely severe, the sudden headache that is highly severe and sudden
- A more severe rupture usually occurs after a leak.
- Pain in the upper and lower part of one eye
- Double vision
- The face is numb on one side.
Causes
The reasons behind brain aneurysms remain elusive; however, various causes can increase the risk. Numerous factors could result in weakness of an arterial wall, which increases the likelihood of developing aneurysms in the brain or rupture. Aneurysms in the brain are more frequent in older people than in children and more frequent among women than men.
Certain risk factors can develop over time, while others are present from birth.
When should you see the doctor?
Aneurysms may appear in any part of the brain, and however, they are most prevalent in arteries located in the brain's base. Brain. If you develop a sudden, extremely severe headache, seek medical attention immediately. Make a call to your local emergency line when someone experiences the sudden onset of a severe headache, cannot speak, or has seizures.
Risk factors
- Older age
- Cigarette smoking
- High blood pressure (hypertension)
- In particular, using cocaine
- Heavy alcohol consumption
- Certain types of aneurysms can develop following head injuries or certain blood infections.
Brain Aneurysm Treatment
- Treatment for a ruptured brain aneurysm
- The surgical clipping
- Endovascular coiling
- Flow diverter surgery
- Unruptured Treatment for aneurysms in the brain
Complications
If an aneurysm in the brain ruptures, the bleeding is usually only several minutes. The blood could cause damage directly to cells around it, and it can harm or destroy other cells. It also raises the pressure within the skull. If the pressure is too high, then the oxygen and blood flow to the brain can be affected to the point where the brain may lose consciousness, or even death could occur.
The complications that may develop after rupture of the aneurysm may include:
- Cerebral vasospasm (reduced blood flow to the brain)
- Hydrocephalus (too much spinal fluid inside the brain)
- Coma
- Permanent brain damage
- It's bleeding again
- Hyponatremia (low sodium levels in your blood)